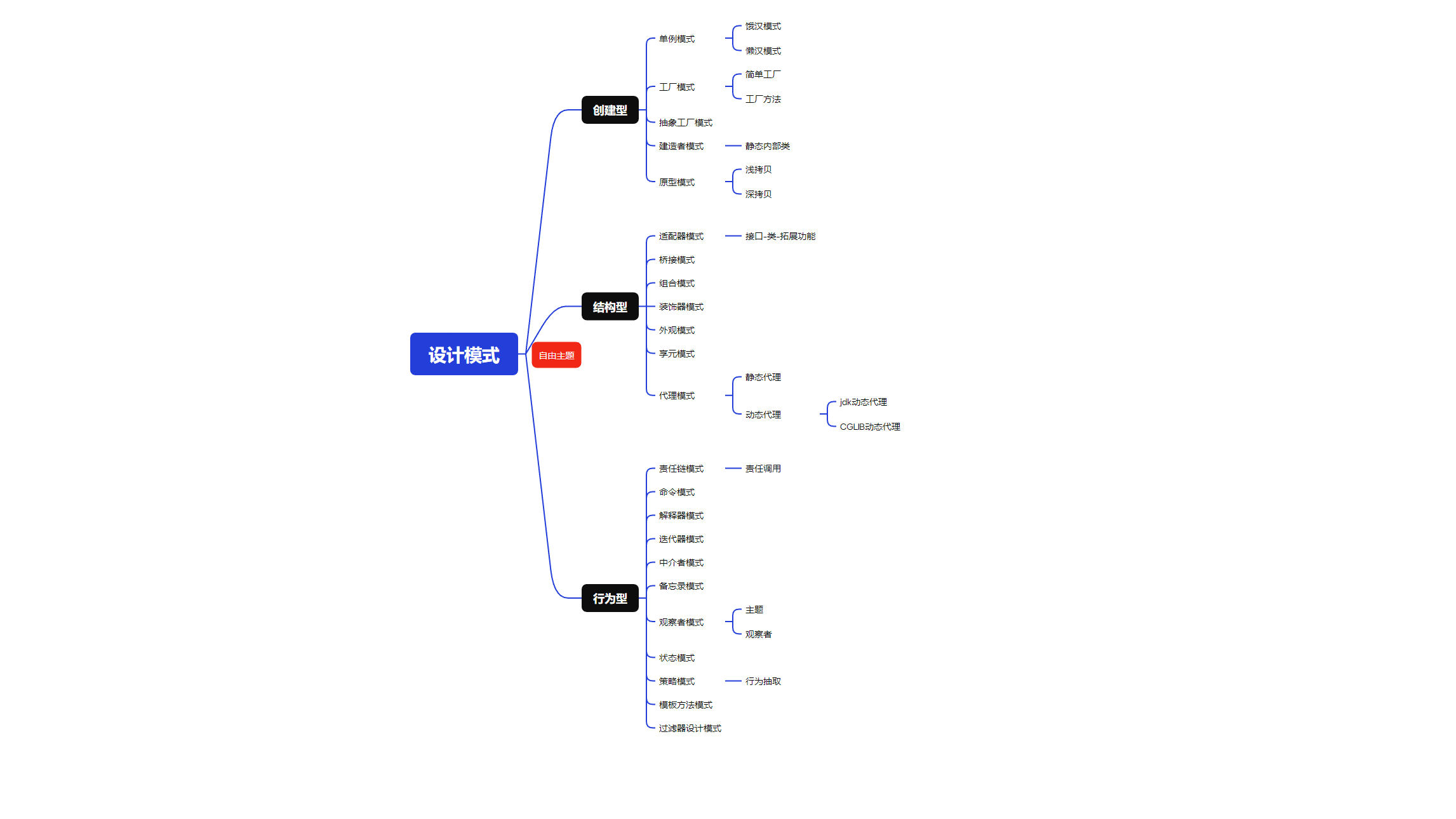
创建型模式 对象的创建
单例模式 一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点来访问这个实例,分为饿汉和懒汉,饿汉是类加载时候创建实例,懒汉是类第一次调用创建实例。
饿汉模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Singleton { private static final Singleton instance = new Singleton (); private Singleton () {} public static Singleton getInstance () { return instance; } }
懒汉模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance; private Singleton () {} public static Singleton getInstance () { if (instance == null ) { instance = new Singleton (); } return instance; } }
工厂模式 工厂模式属于创建型模式,提供创建对象接口,子类决定实现哪一个类。分为简单工厂,工厂方法
简单工厂
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 abstract class Product { public abstract void use () ; } class ConcreteProductA extends Product { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("使用产品A" ); } } class ConcreteProductB extends Product { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("使用产品B" ); } } class SimpleFactory { public static Product createProduct (String type) { if ("A" .equals(type)) { return new ConcreteProductA (); } else if ("B" .equals(type)) { return new ConcreteProductB (); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("未知的产品类型" ); } } } public class FactoryPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Product productA = SimpleFactory.createProduct("A" ); productA.use(); Product productB = SimpleFactory.createProduct("B" ); productB.use(); } }
工厂方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 interface Product { void use () ; } class ConcreteProductA implements Product { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("使用产品A" ); } } class ConcreteProductB implements Product { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("使用产品B" ); } } abstract class Factory { public abstract Product createProduct () ; } class ConcreteFactoryA extends Factory { @Override public Product createProduct () { return new ConcreteProductA (); } } class ConcreteFactoryB extends Factory { @Override public Product createProduct () { return new ConcreteProductB (); } } public class FactoryMethodPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Factory factoryA = new ConcreteFactoryA (); Product productA = factoryA.createProduct(); productA.use(); Factory factoryB = new ConcreteFactoryB (); Product productB = factoryB.createProduct(); productB.use(); } }
抽象工厂 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 interface AbstractProductA { void use () ; } interface AbstractProductB { void use () ; } class ProductA1 implements AbstractProductA { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("使用产品A1" ); } } class ProductB1 implements AbstractProductB { @Override public void use () { System.out.println("使用产品B1" ); } } interface AbstractFactory { AbstractProductA createProductA () ; AbstractProductB createProductB () ; } class ConcreteFactory1 implements AbstractFactory { @Override public AbstractProductA createProductA () { return new ProductA1 (); } @Override public AbstractProductB createProductB () { return new ProductB1 (); } } public class AbstractFactoryPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { AbstractFactory factory1 = new ConcreteFactory1 (); AbstractProductA productA1 = factory1.createProductA(); productA1.use(); AbstractProductB productB1 = factory1.createProductB(); productB1.use(); } }
建造者模式 通过静态内部类实现,解决对象可选构造参数过多问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public class Meal { private String mainCourse; private String drink; private String dessert; private Meal (Builder builder) { this .mainCourse = builder.mainCourse; this .drink = builder.drink; this .dessert = builder.dessert; } public String getMainCourse () { return mainCourse; } public String getDrink () { return drink; } public String getDessert () { return dessert; } public static class Builder { private String mainCourse; private String drink; private String dessert; public Builder (String mainCourse) { this .mainCourse = mainCourse; } public Builder setDrink (String drink) { this .drink = drink; return this ; } public Builder setDessert (String dessert) { this .dessert = dessert; return this ; } public Meal build () { return new Meal (this ); } } } public class BuilderPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Meal meal = new Meal .Builder("牛排" ) .setDrink("橙汁" ) .setDessert("蛋糕" ) .build(); System.out.println("主菜: " + meal.getMainCourse()); System.out.println("饮料: " + meal.getDrink()); System.out.println("甜点: " + meal.getDessert()); } }
原型模式 原型模式是一种创建型模式,不通过new实例化来创建对象,而是通过克隆创建对象。
浅拷贝模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public abstract class Prototype implements Cloneable { protected String name; public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public abstract Prototype clone () ; } public class ConcretePrototype extends Prototype { @Override public Prototype clone () { try { return (Prototype) super .clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { return null ; } } @Override public String toString () { return "ConcretePrototype{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}' ; } } public class PrototypePatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { ConcretePrototype prototype = new ConcretePrototype (); prototype.setName("Prototype 1" ); ConcretePrototype copy = (ConcretePrototype) prototype.clone(); copy.setName("Prototype 2" ); System.out.println(prototype); System.out.println(copy); } }
结构型模式 对象之间的关系
适配器模式 一种结构型设计模式,它允许将不兼容的接口转换为兼容的形式。换句话说,适配器模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的类能够协同工作。这种模式通常用于集成旧系统、第三方库或在不同接口之间进行桥接。
Target(目标接口) :定义客户端所期待使用的接口。Adaptee(被适配者) :已经存在的接口或者类,它的方法需要被适配。Adapter(适配器) :负责实现目标接口,并通过调用被适配者的相应方法来满足目标接口的要求。定义目标接口 MediaPlayer
1 2 3 public interface MediaPlayer { void play (String audioType, String fileName) ; }
创建实现了 MediaPlayer 接口的具体类 AudioPlayer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class AudioPlayer implements MediaPlayer { @Override public void play (String audioType, String fileName) { if ("mp3" .equalsIgnoreCase(audioType)) { System.out.println("Playing mp3 file. Name: " + fileName); } else { System.out.println("Invalid media. " + audioType + " format not supported" ); } } }
定义被适配者接口 AdvancedMediaPlayer
1 2 3 4 public interface AdvancedMediaPlayer { void playVlc (String fileName) ; void playMp4 (String fileName) ; }
创建实现了 AdvancedMediaPlayer 接口的具体类 VlcPlayer 和 Mp4Player
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class VlcPlayer implements AdvancedMediaPlayer { @Override public void playVlc (String fileName) { System.out.println("Playing vlc file. Name: " + fileName); } @Override public void playMp4 (String fileName) { } } public class Mp4Player implements AdvancedMediaPlayer { @Override public void playVlc (String fileName) { } @Override public void playMp4 (String fileName) { System.out.println("Playing mp4 file. Name: " + fileName); } }
创建适配器类 MediaAdapter 实现 MediaPlayer 接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class MediaAdapter implements MediaPlayer { private AdvancedMediaPlayer advancedMusicPlayer; public MediaAdapter (String audioType) { if (audioType.equalsIgnoreCase("vlc" ) ){ advancedMusicPlayer = new VlcPlayer (); } else if (audioType.equalsIgnoreCase("mp4" )){ advancedMusicPlayer = new Mp4Player (); } } @Override public void play (String audioType, String fileName) { if (audioType.equalsIgnoreCase("vlc" )){ advancedMusicPlayer.playVlc(fileName); }else if (audioType.equalsIgnoreCase("mp4" )){ advancedMusicPlayer.playMp4(fileName); } } }
修改 AudioPlayer 类以支持适配器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class AudioPlayer implements MediaPlayer { private MediaAdapter mediaAdapter; @Override public void play (String audioType, String fileName) { if ("mp3" .equalsIgnoreCase(audioType)) { System.out.println("Playing mp3 file. Name: " + fileName); } else if ("vlc" .equalsIgnoreCase(audioType) || "mp4" .equalsIgnoreCase(audioType)){ mediaAdapter = new MediaAdapter (audioType); mediaAdapter.play(audioType, fileName); } else { System.out.println("Invalid media. " + audioType + " format not supported" ); } } }
测试适配器模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class AdapterPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { AudioPlayer audioPlayer = new AudioPlayer (); audioPlayer.play("mp3" , "beyond the horizon.mp3" ); audioPlayer.play("mp4" , "alone.mp4" ); audioPlayer.play("vlc" , "far far away.vlc" ); audioPlayer.play("avi" , "mind me.avi" ); } }
输出结果:
1 2 3 4 Playing mp3 file. Name: beyond the horizon.mp3 Playing mp4 file. Name: alone.mp4 Playing vlc file. Name: far far away.vlc Invalid media. avi format not supported
代理模式 中间类,代理模式分为静态代理和动态代理,静态代理是在编译就创建代理类,明确知道要代理谁,动态代理是在允许的时候创建代理类,谁调用就代理谁,哪个实例传入就代理谁。动态代理分为jdk动态代理和cglib动态代理,区别是jdk代理类需要实现接口,基于接口,cglib需要第三方库。
静态代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public interface Service { void doSomething () ; } public class ServiceImpl implements Service { @Override public void doSomething () { System.out.println("执行业务逻辑" ); } } public class ServiceProxy implements Service { private final Service realService; public ServiceProxy (Service realService) { this .realService = realService; } @Override public void doSomething () { System.out.println("准备执行业务逻辑..." ); realService.doSomething(); System.out.println("业务逻辑执行完毕!" ); } } public class StaticProxyDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { Service realService = new ServiceImpl (); Service proxyService = new ServiceProxy (realService); proxyService.doSomething(); } }
jdk动态代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class DynamicProxyHandler implements InvocationHandler { private final Object target; public DynamicProxyHandler (Object target) { this .target = target; } @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("准备执行业务逻辑..." ); Object result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("业务逻辑执行完毕!" ); return result; } public static void main (String[] args) { Service realService = new ServiceImpl (); Service proxyService = (Service) Proxy.newProxyInstance( realService.getClass().getClassLoader(), realService.getClass().getInterfaces(), new DynamicProxyHandler (realService)); proxyService.doSomething(); } }
cglib动态代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class CglibProxyFactory implements MethodInterceptor { private final Object target; public CglibProxyFactory (Object target) { this .target = target; } public Object getProxy () { Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer (); enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass()); enhancer.setCallback(this ); return enhancer.create(); } @Override public Object intercept (Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable { System.out.println("准备执行业务逻辑..." ); Object result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("业务逻辑执行完毕!" ); return result; } public static void main (String[] args) { ServiceImpl realService = new ServiceImpl (); CglibProxyFactory proxyFactory = new CglibProxyFactory (realService); ServiceImpl proxyService = (ServiceImpl) proxyFactory.getProxy(); proxyService.doSomething(); } }
行为型模式 对象之间的通讯与协作
观察者模式 主题内容改变,下面的观察者可以接收主题内数据改变消息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 interface Observer { void update (float temp) ; } interface Subject { void registerObserver (Observer o) ; void removeObserver (Observer o) ; void notifyObservers () ; } class WeatherData implements Subject { private List<Observer> observers; private float temperature; public WeatherData () { observers = new ArrayList <>(); } @Override public void registerObserver (Observer o) { observers.add(o); } @Override public void removeObserver (Observer o) { observers.remove(o); } @Override public void notifyObservers () { for (Observer observer : observers) { observer.update(temperature); } } public void measurementsChanged () { notifyObservers(); } public void setMeasurements (float temperature) { this .temperature = temperature; measurementsChanged(); } } class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer { @Override public void update (float temp) { System.out.println("当前温度:" + temp); } }
实现调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class ObserverPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData (); CurrentConditionsDisplay currentConditionsDisplay = new CurrentConditionsDisplay (); weatherData.registerObserver(currentConditionsDisplay); weatherData.setMeasurements(27.5f ); weatherData.setMeasurements(30.0f ); } }
策略模式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 interface PaymentStrategy { void pay (int amount) ; } class CreditCardPayment implements PaymentStrategy { private String name; private String cardNumber; public CreditCardPayment (String nm, String ccNum) { this .name = nm; this .cardNumber = ccNum; } @Override public void pay (int amount) { System.out.println(amount + " paid using credit/debit card." ); } } class PayPalPayment implements PaymentStrategy { private String emailId; public PayPalPayment (String email) { this .emailId = email; } @Override public void pay (int amount) { System.out.println(amount + " paid using PayPal." ); } } class ShoppingCart { private PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy; public void setPaymentStrategy (PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy) { this .paymentStrategy = paymentStrategy; } public void checkout (int amount) { if (paymentStrategy == null ) { System.out.println("No payment strategy set" ); return ; } paymentStrategy.pay(amount); } } public class StrategyPatternDemo { public static void main (String[] args) { ShoppingCart cart = new ShoppingCart (); cart.setPaymentStrategy(new CreditCardPayment ("John Doe" , "1234567890123456" )); cart.checkout(100 ); cart.setPaymentStrategy(new PayPalPayment ("john.doe@example.com" )); cart.checkout(50 ); } }
责任链模式 Step 1: 定义请求类(LeaveRequest)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class LeaveRequest { private String studentName; private int days; public LeaveRequest (String studentName, int days) { this .studentName = studentName; this .days = days; } public String getStudentName () { return studentName; } public int getDays () { return days; } }
Step 2: 定义处理器接口(Approver)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 abstract class Approver { protected Approver nextApprover; public void setNextApprover (Approver nextApprover) { this .nextApprover = nextApprover; } public abstract void approve (LeaveRequest request) ; }
Step 3: 定义具体的审批人(Concrete Handlers)
班主任(ClassTeacher)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class ClassTeacher extends Approver { @Override public void approve (LeaveRequest request) { if (request.getDays() <= 3 ) { System.out.println("【班主任】批准了 " + request.getStudentName() + " 的请假申请(" + request.getDays() + " 天)" ); } else if (nextApprover != null ) { System.out.println("【班主任】无权审批,请假天数超过权限范围,转交给下一级审批人..." ); nextApprover.approve(request); } } }
年级主任(GradeDirector)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class GradeDirector extends Approver { @Override public void approve (LeaveRequest request) { if (request.getDays() > 3 && request.getDays() <= 7 ) { System.out.println("【年级主任】批准了 " + request.getStudentName() + " 的请假申请(" + request.getDays() + " 天)" ); } else if (nextApprover != null ) { System.out.println("【年级主任】无权审批,请假天数超过权限范围,转交给下一级审批人..." ); nextApprover.approve(request); } } }
校长(Principal)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Principal extends Approver { @Override public void approve (LeaveRequest request) { if (request.getDays() > 7 ) { System.out.println("【校长】批准了 " + request.getStudentName() + " 的请假申请(" + request.getDays() + " 天)" ); } else if (nextApprover != null ) { nextApprover.approve(request); } else { System.out.println("没有合适的审批人,请假申请未被处理。" ); } } }
Step 4: 编写测试类(Client)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Client { public static void main (String[] args) { Approver classTeacher = new ClassTeacher (); Approver gradeDirector = new GradeDirector (); Approver principal = new Principal (); classTeacher.setNextApprover(gradeDirector); gradeDirector.setNextApprover(principal); LeaveRequest request1 = new LeaveRequest ("张三" , 2 ); LeaveRequest request2 = new LeaveRequest ("李四" , 5 ); LeaveRequest request3 = new LeaveRequest ("王五" , 10 ); System.out.println("---------- 开始处理请假申请 ----------" ); classTeacher.approve(request1); classTeacher.approve(request2); classTeacher.approve(request3); } }
📌 输出结果
运行上面的程序后,输出如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ---------- 开始处理请假申请 ---------- 【班主任】批准了 张三 的请假申请(2 天) 【班主任】无权审批,请假天数超过权限范围,转交给下一级审批人... 【年级主任】批准了 李四 的请假申请(5 天) 【班主任】无权审批,请假天数超过权限范围,转交给下一级审批人... 【年级主任】无权审批,请假天数超过权限范围,转交给下一级审批人... 【校长】批准了 王五 的请假申请(10 天)